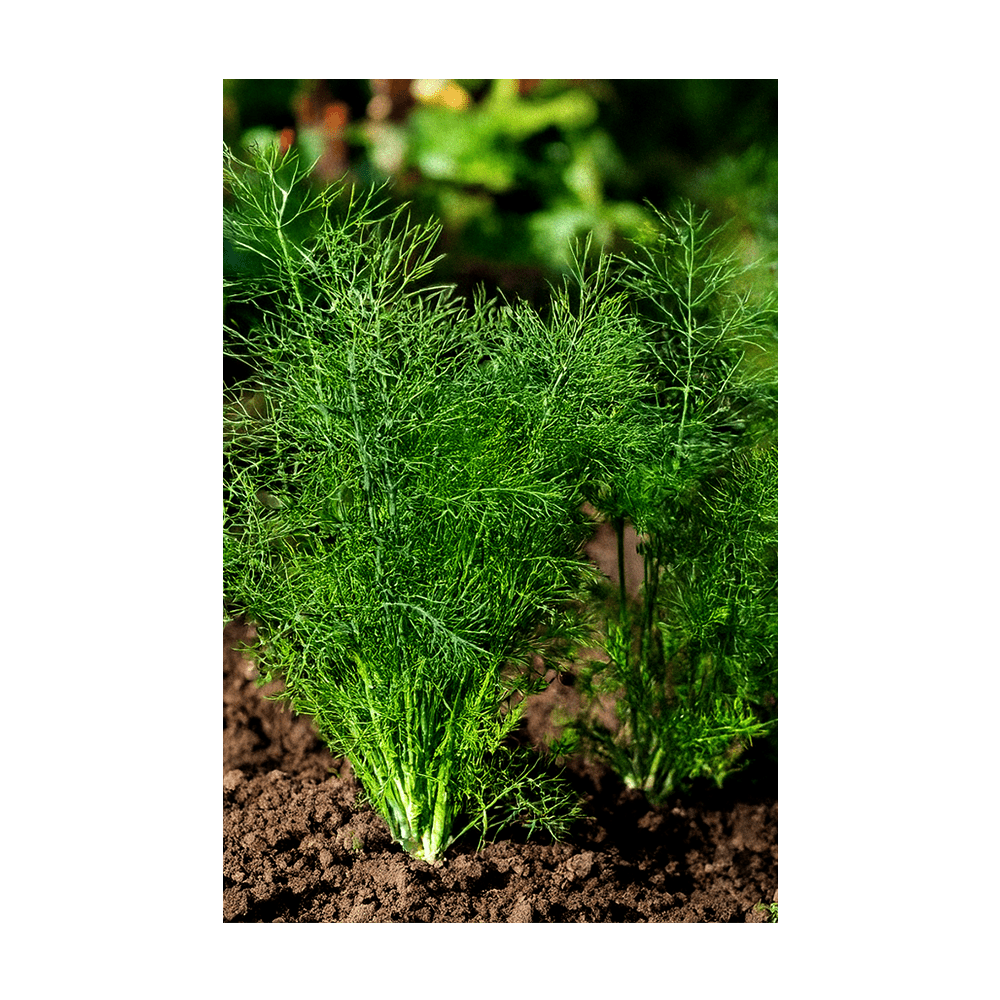
Dill Herb Seeds Packet
Couldn't load pickup availability
We stand by the quality of our flower seed packets! With high germination rates and vibrant blooms, your garden is sure to flourish. If you're not completely satisfied, we’ll replace or refund—guaranteed!
Why Shido Seeds Are the Best
Our flower and vegetable seeds are beautifully packaged little packets of magic. Guaranteed to turn your garden into the envy of the neighborhood. Get your hands dirty and let nature simply do its thing.
How to Plant Dill from Seed
When to Plant Seeds
Preparing for Planting
Direct Sowing Outdoors
Indoor Starting
Pro Tip

Getting to know your Dill
What it's used for
Growth Requirements
Maintenance
Pests and Diseases

Growing Together with Shido
At Shido, everything we do starts with one goal: helping you have a truly successful growing experience. We know that planting seeds is just the beginning — your time, energy, and love for gardening are the real magic. That’s why we make sure the seeds you plant are fresh, full of life, and top-quality. When you choose Shido, you’re planting with confidence. We guarantee it.
Our mission is simple: bring you exceptional varieties of high-quality seeds at prices you’ll love, share detailed sowing and growing tips so you can thrive as a home gardener, and deliver the best customer service in the industry — with a smile.
Our Seed Safety Promise
We do not sell genetically modified seeds — ever. And we don’t use genetic engineering to breed new varieties. Instead, our skilled breeders use traditional, natural crossing methods to create hybrid seeds that are healthy, safe, and packed with potential.
Our Seed Quality Guarantee
At Shido, we believe great gardens start with great seeds — and that means quality comes first. Every seed lot we offer is ensure to generate top-notch germination because your garden deserves nothing less.
To keep our seeds at their peak, we run thorough pathology tests at trusted outside labs. When you open a Shido seed packet, you can trust it’s been nurtured, tested, and approved to give you strong, healthy plants from the very first sprout.
Types of Seeds We Offer
Hybrid Seeds (F1)
F1 hybrid seeds are the garden’s high achievers — created by crossing two specially chosen parent plants for superior vigor, uniformity, and performance. We use only traditional breeding methods to produce these powerhouse seeds.
Open-Pollinated & Heirloom Seeds
Our open-pollinated (OP) seeds naturally reproduce through wind, insects, water, or self-pollination. When grown in isolation, they produce true-to-type plants year after year.
Among our OP seeds are treasured heirloom varieties — old favorites that have been carefully passed down for generations. While OP plants can be less uniform than hybrids, we run our Open-Pollinated Project to select the most reliable, flavorful, and beautiful strains. Many are also available as certified organic seeds.
Non-GMO: What It Means and Why It Matters
A GMO (Genetically Modified Organism) is created when scientists alter a plant’s DNA in a lab — often by inserting genes from completely unrelated species — to achieve certain traits, like pest resistance or herbicide tolerance. This is a far cry from natural plant breeding.
At Shido, we believe gardening should stay as close to nature as possible. All our seeds — whether hybrid, heirloom, organic, or open-pollinated — are Non-GMO. They’re bred using traditional methods that respect natural biodiversity, giving you safe, wholesome seeds that grow into plants just as nature intended.
When you plant Shido Non-GMO seeds, you’re choosing purity, sustainability, and peace of mind — along with a garden full of flavor, color, and beauty.
Vacuum-Sealed for Freshness — Good for 10 Years
Every Shido seed packet is vacuum-sealed to lock in freshness and protect your seeds from moisture, air, and pests. This careful packaging not only preserves their quality but also extends their shelf life dramatically. Stored properly in a cool, dry place, our seeds remain viable for up to 10 years — so you can plant them now, next season, or even years down the road. Whether you’re planning a garden this spring or building a long-term seed stash, Shido seeds are ready when you are.
Feed Your Plants Like You Actually Know What You’re Doing
Your plants called—they're tired of your "just water and hope" approach. Give them VerteRx, the premium plant food packed with vitamins and growth boosters. Stronger roots, lusher leaves, and fewer judgmental stares from your fiddle-leaf fig. Because even plants deserve proper nutrition (unlike your diet).